Autocad Tutorial 6 easy steps to learn AutoCAD
AutoCAD Tutorial

In this AutoCAD tutorial, you are going to learn the basics of how to use AutoCAD and create your first objects. AutoCAD is a vrey useful tool to create 2D and 3D objects, like architectural floorplans and constructions or engineering projects. It can also generate files for 3D printing.
In this AutoCAD tutorial for beginners, you’ll learn folowing steps:
Step 1: How to install the software
Step 2: Basic orientation in AutoCAD
Step 3: How to sketch in 2D
Step 4: How to model in 3D
Step 5: .stl and Mesh-Files in AutoCAD
Step 6: How Create a technical drawing from a 3D object
Step 1. Installing the Software
In the first step, we will learn how to install the software.
➤ 1.1 Create an AutoDesk Account
AutoCAD is a Computer Aided Design software developed by AutoDesk Inc., is the most popular PC-CAD system available in market. Today over 7 million people are using AutoCAD and other AutoCAD-based design products.
➤ 1.2 Installing the software
After you have installed AutoCAD, an AutoCAD icon is displayed on the dekstop.You can start AutoCAD by double-clicking on it. You can also start AutoCAD using the start menu by choosing the start button at the bottom left corner of the screen (default option).On doing so, a menu will be displayed. From this menu, choose programs to display program folders. Now, choose Autodesk > AutoCAD 2019 folder to display AutoCAD program and then choose AutoCAD 2019-ENGLISH to start AutoCAD.
- Double click on the installation file, and then click 'yes' to complete the installation.
- Click on 'install'.
- Check the box 'I agree' and then click 'next'.
- For the standalone License type default option, enter the serial key & product key detail found on the software database of this software version.
- Click 'Install'.
- Click 'finish' to complete installation.
 |
Installing AutoCAD |
Step 2. Basic Orientation
AutoCAD comes with baic ribbon tools which basically contains drawing tools, modification tools and controls. The infocenter search tool bar is displayed at the top right-hand corner. You will find the command window at the bottom of drawing window.
The second step of this AutoCAD Tutorial, teaches how to interact with the workspace.
➤ 2.1 Set Up the AutoCAD Workspace

When you are opening the AutoCAD, click on “Start Drawing” to open a new file or project. By doing this, “DrawSpace” will be opened.
Firstly, you have to customize the Quick Action Toolbar and add “Workspace”. Now change the new Toolbar “Drafting and Annotation” to “3D Modelling”.
➤ 2.2 Change Units
If you want to change units to the metric system you have to, click on the big red A in the top left corner. Now AutoCAD menu will be opened. Select “Drawing Utilities” > “Units”. Change the Insertion Scale to Millimeters.
➤ 2.3 Explanation of the WorkspacE
Workspace are mainly the sets of menus, toolbar, platters, and ribbon control panels that are grouped and organised so that you can work in custom, task oriented drawing environment.
2.3.1 THE COMMAND BAR
At the bottom of the DrawSpace, Command Bar will be displayed. You can either enter the commands simply by typing in the command bar. It will show you the options you got for the given command. The highlighted letters are shortcuts to those options.
When you type the corresponding letter and press “Enter” it will directly activate the desired option. It will also list the order of steps you will need to execute the command correctly and display tips.
2.3.2 ORIENTATION IN AUTOCAD
2.3.2 ORIENTATION IN AUTOCAD
In the top right-hand corner of your DrawSpace, you see a compass. It is set to “Top view” right by default over it, and You will see now a little house symbol appear. Click on that to enter isometric view. Now you will see a 3D Cartesian coordinate system in the middle of the DrawSpace with three axes. In which the x-axis is represented in red, Y-Axis in green and Z-Axis in blue.
 |
| Adjust scale seperately in x axis and y axis |
Also, the compass got extended by a cube. You can click on the faces, edges, and corners of the cube to enter the desired view. To pan the DrawSpace click on the “Hand” symbol or move around by holding down the mouse wheel. If you want to orbit your DrawSpace, click on “Orbit” in the right-hand toolbar. Click and hold on the DrawSpace to rotate around the center of the coordinate system by moving your mouse. You can also do so by holding the “Shift” key and the mouse wheel. If you want to orbit around a certain point, select “Free Orbit” by clicking on the extend arrow.
Step 3. How to sketch in 2D
In the third step, you will learn how to sketch in 2D.
➤ 3.1 Set up Snapping
After disolaying the grid, you need to turn on the snap mode so that the cursor snaps to the snap point. The snap points are the invisible points that are created at the intersection of the invisible horizontal and verticle lines.
➤ 3.2 Drawing a Line
 |
Drawing lines in sketching |
In order to create first sketch, select Top View. Disable Grid Snap by pressing F9. Now type “line” and press Enter. This will enable the Line command.
In AutoCAD, we can simply type in the first letters of command. The software will show the available commands. When you have entered the line command, it asks you to specify the first point. You can now either select a random point in your DrawSpace or enter the coordinates. Now enter 0 for X-Coordinate, change to Y-Coordinate by pressing Tab, enter 0 and confirm your coordinates by pressing Enter. The center of the coordinate system as Start is now selected.
Now move your mouse to the positive side of the X-Axis. he coordinate input changed to Polar coordinates. For the length of the line enter 25 by pressing Tab you can switch to the angular input. Try sketching a square for starting. Press Escape to end the line command when you have returned to the cente .
➤ 3.3 Select an Object
➤ 3.4 Drawing Tools
AutoCAD offers several ways to draw a square or rectangle. Select your entire rectangle by marking it. Click on the far outside of your rectangle once. It enables rectangular selection. If you click and hold you can lasso around the entity, you want to select. Press the Delete Button on your keyboard or type “Delete” to remove the selected lines.
In the upper toolbar, you can find all drawing tools. Either you can type in the command or click on the tool you want to use in the next steps. Coordinates, angles, and values are separated.
3.4.1 DRAWING BASIC SHAPES AND EDIT SKETCHES
Start a center ellipse at 0/30. Set parallel the major radius to the X-Axis to 70 and set the minor radius to 30.
3.4.2 DRAW A SECOND CIRCLE WITH OBJECT SNAP ENABLED
Draw a second circle at 25/47.5. The Object Snap is turned on by pressing F3 and guide the radius of the circle parallel to the Y-Axis until you intersect with the ellipse. Click when you see a green Cross. Now draw a line starting at 10/55, you may want to turn off Object Snap, so the starting point will not get caught at the corner of the rectangle. When the starting point is placed turn on, Object Snap with the “Tangent” option enabled.
Draw a line at a 65° angle until it snaps with the second circle. Start a second line at the top right corner of the rectangle and enable “Nearest” in Object Snap option draw a line in a 130° angle, snapping to the first circle.
Draw a line at a 65° angle until it snaps with the second circle. Start a second line at the top right corner of the rectangle and enable “Nearest” in Object Snap option draw a line in a 130° angle, snapping to the first circle.
3.4.3 DRAWING WITH THE SPLINE COMMAND FOR BEGINNERS
Create a Spline starting at the center point. You can create a continuous curved sine connecting point with the help of Spline tools . First, you enter the distance, followed by the angle. If you made a mistake type in “U” and press Enter to undo the last step. Enter the following polar coordinates: 20/30°, 5/300°, 5/55°, 10/30°, 5/320°. End with 230° Angle on the Ellipse. Now type in a “T” to End Tangency and type in 190° for the angle and press Enter.
3.4.4 TRIM ENTITIES
By using the Trim command, you can remove extra lines up to an intersection. You can also switch within the Trim command to “Erase” by typing R. This will remove lines which are not intersecting like the Delete command.
Start the Trim command and press Enter to select the entire Sketch for trimming. Trim the overhanging lines. If you removed a line by mistake type in “U” to Undo. Take a close look at any lines stuck in between small edges. Those will most likely trouble in the extrusion process which will make your sketch 3D. Confirm with Enter when you finished.
Next, select the line in the middle and the spare ellipse on the left and delete them. Finally, highlight the tiny ellipse line in the upper triangle and delete it as well.
After finishing Trimming and Erasing you should end up with this.
After Trimming and Erasing you should end up with this.
3.4.5 MIRROR A SKETCH
When drawing symmetrical sketches, it comes in handy to simply draw one-half of the sketch and mirror it afterward. Type “Mirror” or select Mirror in the Modify toolbar. Then mark the entire sketch and confirm with Enter. Now Select CenterPoint as the first point of mirror line and for the second point a positive coordinate along the Y-Axis. Click “No” on the question to remove source object.
Step 4. Modeling 3D Objects
When working with 3D, you have to remember, that drawing in AutoCAD is only done on the XY-Plane. In order to change the direction to draw or plot your 3D object, you must redefine the coordinate system. Draw a random circle in your DrawSpace while being in Top view. Now enter Front view and type “UCS”. This will allow you to set a new coordinate system. Type “V” to set your new coordinate system as the current view. Draw a second circle concentric with the first one. By holding Shift rotate the model and the mouse wheel, Then the 3D alignment of both circles will be displayed.
➤ 4.1 3D Build Basic Shapes
4.1.1. PREDEFINED 3D OBJECT
You can also build predefined 3D Objects with AutoCAD such as Cubes, Cylinders, Balls or Pyramids on the current plane you are drawing on or onto an objects face, edge or corner. Set you coordinate system back by using the UCS command. Switch to the isometric view and type “Cylinder".Now draw the base of the cylinder and click when it has the desired radius. Now extrude the cylinder by moving your mouse upside. You can enter a value for the height as well. Confirm by pressing enter. You can draw other basic shapes just as easy.
4.1.2 EXTRUDE FEATURE IN AUTOCAD
AutoCAD Tutorial – How to extrude objects
You can also extrude your sketches with the Extrude feature.Let's draw a Polygon and set it's edges to 8. Then chose CenterPoint as the center, and choose between Circumscribed or Inscribed. After finishing the Polygon type “Extrude.” Select the Polygon as a base. Type in “Mode” followed by “Solid” to create a solid 3D Object. Then set the height of the object. By double-clicking the object you can change the height.
➤ 4.1.3 Chamfer and Fillet Feature
The corners and dges can be easily smoothed or chamfered. Switch to the Solid tab and click on Fillet Edge. Now you have to select all the top edges of the polygon. If you want to lower the effort select all the edges manually, type in “Loop”. Then click on one top edge. And click next to flip through the possible edge connections. As a result all the top edges are highlighted, click accept and type “Radius” to define the size of the Fillet. You can also try out several values and preview the fillet. Click or type in radius again to change it. To accept the previewed fillet press enter two times.
Now turn the polygon around and select with the arrow under the fillet feature the chamfer feature. Type Loop and then select one bottom edge of the polygon. Click Next until the lower rim of the polygon is highlighted. Now click distance and type the first length of the chamfer. Then confirm it by pressing enter and type in the second length. Once again you can see a preview and hit enter two times to confirm.
4.1.4 CHANGE VISUALS OF 3D OBJECTS IN AUTOCAD
To change the visual effects when displaying 3D objects, you can do so by typing VISUALSTYLE. The visual style can be changed from 2D Wireframe to Shades of Grey or whatever style you favor.
➤ 4.2 Merge, subtract and intersect 3D Objects
4.2.1 MERGE OBJECTS
Right on top of a cylinder draw a sphere of same radius. Now type “Union” select the sphere and the cylinder. Confirm it with Enter. Over both shapes you will see that they have become one solid object.
AutoCAD Tutorial – How to merge objects
4.2.2 SUBTRACT OBJECTS
4.2.3 INTERSECT OBJECTS
With the single sphere and cylinder start again. Now type “Intersect” and select both objects and confirm.
AutoCAD Tutorial – Intersect Objects
➤ 4.3 Sweep, Loft, and Revolve Feature
4.3.1 SWEEP FEATURE
AutoCAD Tutorial – Sweep Feature
Sweep Feature involves designing complex curved structures. You can add a nice detail to your design by twisting it. In AutoCAD to do sweep, you need to sketch the base geometry of your sweep first. Draw a polygon on the CenterPoint which has 8 edges. Now set the UCS to Front view and draw an Arc from the CenterPoint. This will be the Sweep Path. It must not cross nor can it be too close to itself. Now type in “Sweep,” select the circle as base and confirm. Then type in “Twist,” followed by 180 or any angle you want to twist the structure. If you don’t want to twist the sweep you do not need to do that. Select the arc as Sweep Path.
4.3.2 LOFT FEATURE
Draw a circle on the CenterPoint with a radius of 100. Switch to Front view and set the CenterPoint of an 8-edged polygon on 0/0/50. Switch back to Top view and finish the polygon circumscribed by a radius of 100. Start “Loft” Command and select the circle and then the polygon. Type in “Mode” and select Solid. Press Enter and click on “Cross Sections only”. |
Loft feature |
The Revolve Feature is an way to design objects uncomplicately with line symmetry. You can start by sketching the object you want to revolve. Draw a line at the CenterPoint and follow Y-axis. Except the center line select everythingand confirm. Now select one endpoint of the center line and then the other one. It will define the rotation axis. You can also type Y, as the Y-Axis is the rotation axis in this sketch. Now set the Angle to 270° and confirm. The object will be solid only if you do a 360 rotation.
➤ 5.1 Import .stl and other Mesh-Files
AutoCAD can work with the standardized ISO format STEP but it cannot import Mesh-Files. .step and Autodesk’s interchange format .dxf. To generate these file types you can use other AutoCAD software like Inventor or free software like FreeCAD. Here is a quick way upload the .stl to a converter provided by CAD-Forum and generate a .dxf file.
First create a new Drawing then open .dxf files in AutoCAD . Now click on the AutoCAD logo > Open > Drawing and select .dxf in the file browser as file type. You can change the visual style by typing VISUALSTYLE when the model is imported.
➤ 5.2 Export .stl
➤ 5.2 Export .stl
Luckily in AutoCAD exporting .stl files is possible. For that click on the AutoCAD logo > Export > Other File Formats and select .stl in the file browser as the file type.
Step 6. Create Technical Drawings
To create a technical drawing of the model you created, AutoCAD is the best software to work with. Firstly, you will need a template sheet for the technical drawing. For template sheet click templates on the AutoCAD website for free.Download the Manufacturing Metric template then, open the object from which you want to create a technical drawing. Then right-click on + in the bottom left corner and now open the downloaded template. Here by double-clickingyou can insert your name, project or other related information into the title block in the bottom right of the sheet.
➤ 6.1 Insert Model View
In the drawing sheet template tab, From Model Space click on base.
Click to place the first view (which is the front view) in the middle of your sheet. Once you clicked, you can now select orientation to switch to a different view. If the model is too large or small, then you should click on Scale and select a scaling factor. Click on Move to position the object.
To accept left-Click at the desired position. Now you can continue to place other views by dragging the mouse horizontally or vertically. To confirm each position click left button of mouse. When you move the object to a 45° angle, you can place the isometric view. Always try to place enough views of the object so most or all of the features can be seen. By selecting one view, you can move it with the blue square and size it with the blue triangle.
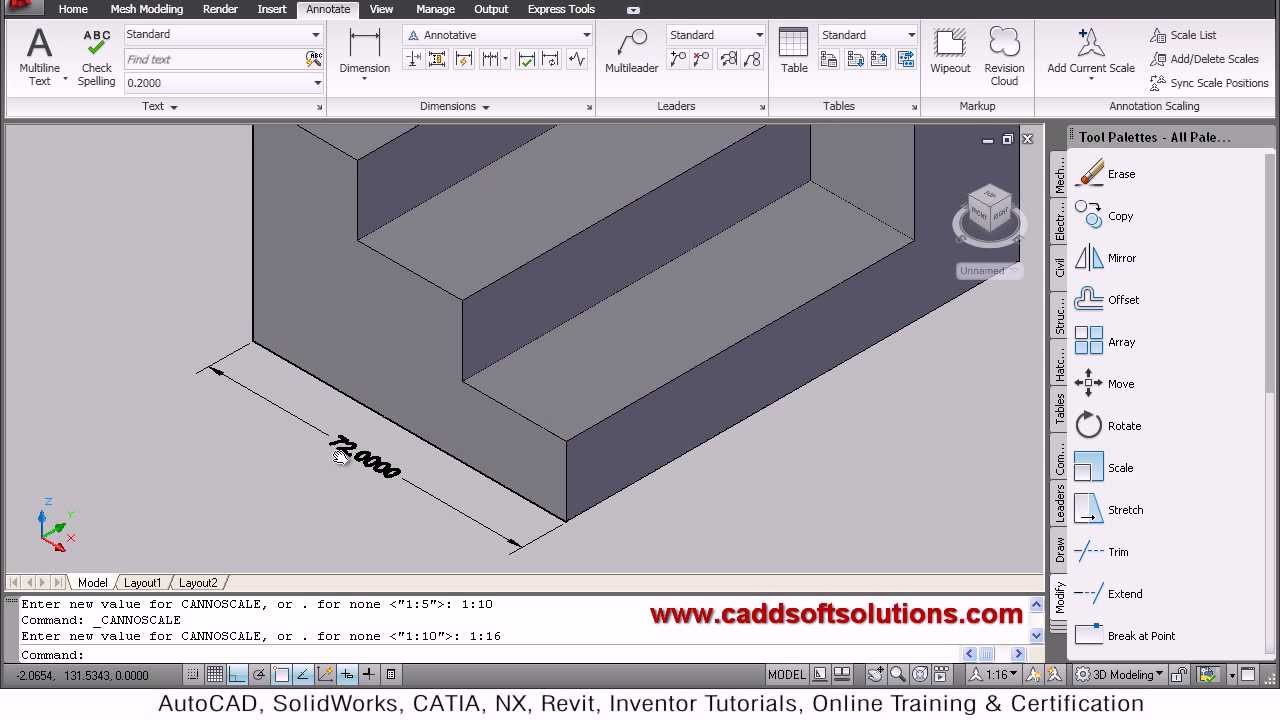
You have to follow three basic rules while placing dimensions:
- Start with the smallest detail
- Annotate a detail only once
- Annotate every detail
- Switch to the Annotation tab to start annotating. Now select the Dimension command. This is a smart command it adapts to the feature you want to annotate. Now select themtwo dots or first line you want to describe. You can see the length or radius, and can move the annotation into position. Position the annotation, so it does not intercept with other lines, numbers or is too close to the object itself.
In order to dimension circles or holes, you have to place first a center mark. To select a circle click on Center Mark in the annotation tab . To annotate the circle use the dimension command. By typing R or D on your keyboard you can switch between Radius and Diameter.
➤ 6.3 Detail and Section View
Click on Layout > Detail > Circular to place a detail view of your drawing. Now, select the parent view you want to specify followed by clicking in the middle of the detail to set a center point. Now you have to draw a circle enclosing the detail and place the detailed view at a free spot.
To look inside a drawing, you should use Layout > Section View. Select the view you want to create followed by selecting two points for the section line. Confirm it by pressing enter and place the section view at a free spot. The size and line style can be changed afterward.
➤ 6.3 Detail and Section View
















Comments
Post a Comment